How can I prepare for the exam?
The X-Ray exam is quick and painless and usually requires no special preparation.
What should I expect during the exam?
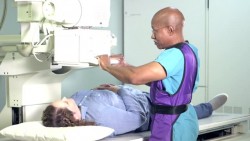
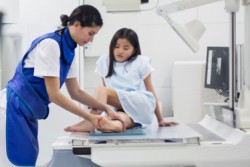
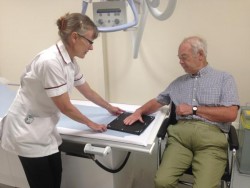
You may be asked to lie down on a table, sit in a chair, or stand. A technologist will help position you properly. The exam will take around 15 minutes.
Is the X-Ray exam safe?
Yes. We always use the minimum amount of radiation necessary to create a quality image. The benefit of an accurate diagnosis far outweighs the small risk. Please let the technologist know if you are pregnant.
What are some common types of X-Ray exams?
X-Ray technology is highly adaptable and can be quite effective in helping to diagnose disease or injury, depending on which part of your body is being scanned. The following are the most common types of X-Ray exams:
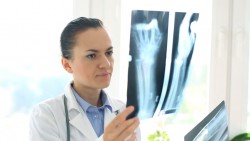
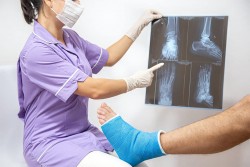
- Bone X-Rays are recommended for viewing the skeletal system. This simple imaging procedure, which uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation, aids doctors in diagnosing fractured bones or joint dislocation. Bone X-Rays can help guide faster and less-invasive treatment for injuries.
- Chest X-Rays are commonly used to evaluate the lungs, heart and chest wall. This procedure can help your provider evaluate symptoms such as shortness of breath, persistent cough, fever and chest pain. Chest X-rays are also used to diagnose a variety of lung conditions, including pneumonia, emphysema and cancer, monitor the effectiveness of treatments and for quick and accurate diagnoses in emergency trauma care.
- Abdominal X-Rays are used to evaluate the stomach, liver, intestines and spleen and can help doctors diagnose the root cause of symptoms like unexplained pain, nausea or vomiting. A more specialized version of abdominal X-Rays, called KUB X-Rays, are used to examine the kidneys, ureters and bladder.
- Upper GI X-Rays use a form of real-time X-Ray imaging called fluoroscopy to examine the upper gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Prior to, or during an upper GI X-Ray, a barium-based contrast liquid is consumed to help produce images of your esophagus, stomach and small intestine. This type of X-Ray exam is safe, noninvasive and can be used to help accurately diagnose the cause of digestive symptoms such as pain, acid reflux and more.
- Lower GI X-Rays are almost identical to Upper GI X-Rays in their application and function and help doctors to detect disease and abnormalities in your digestive system that cause symptoms like pain, constipation or blood in the stool. A Lower GI X-Ray will often provide specialists with enough information to avoid more invasive procedures like a colonoscopy.
Further questions?
We want to help guide you through every step of the process, so if you have any further questions or concerns about your exam, please feel free to contact us at (702) 550-2748.
Schedule